 OVERVIEW
OVERVIEW
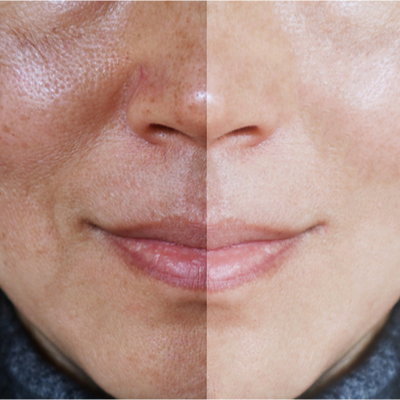
If you notice a sudden unevenness in skin tone with darker or darkened patches of skin, you may have a common skin condition known as melasma.
If melasma has you feeling less confident about your appearance, scheduling an appointment with a board-certified dermatologist can help you correctly diagnose and treat this commonly-occurring skin disorder.
What is Melasma?
Affecting the face and neck, melasma is a skin condition that results in areas of skin becoming darker or hyperpigmented.
While melasma can occur in people of all skin tones, research shows that it predominantly affects people of color. Melasma also typically affects women more than men and commonly appears during pregnancy or while on oral contraceptives.
What are the Causes of Melasma?
Melasma happens when melanocytes—the skin cells responsible for producing melanin, the brown pigment that gives your skin its color—are made to produce excess melanin than usual.
Melasma can happen due to several different reasons, including:
- Exposure to the sun and UV radiation
- Pregnancy
- Oral contraceptives
- Hormone therapy
- Cosmetics
- Certain medications like anti-seizure medicines
- Family history of the condition
What are the Symptoms of Melasma?
Melasma is a commonly occurring skin condition that results in brown or grayish-brown patches of skin on your forehead, cheeks, upper lip, chin, and jaw.
It frequently occurs in women more than men as melanin production is stimulated by the female sex hormones estrogen and progesterone. Melasma, if it happens during pregnancy, is sometimes referred to as a “pregnancy mask” or “chloasma.”
How is Diagnosed?
It’s not uncommon for melasma to go away on its own—especially if you’re pregnant and experiencing symptoms. However, for others, melasma can be a lifelong condition, which some people may want to treat for cosmetic reasons.
A board-certified dermatologist can accurately diagnose melasma by conducting a thorough examination, including evaluating your overall health and family history of the disorder.
To rule out several other skin conditions with similar symptoms, your dermatologist may also use a Wood’s lamp (which has UV light) to visualize the pigment on your skin or perform a skin biopsy.
Treatment for Melasma is Safe When Performed by a Board-Certified Dermatologist
Depending on your symptoms, a dermatologist can prescribe one or more of the following methods of treatment for your melasma:
- Use a sunscreen that contains iron oxide, zinc oxide, or titanium dioxide
- Topical treatments such as hydroquinone cream, which prevent the production of melanin
- Chemical peels
- Laser treatment, especially if your melasma is severe


